Data Type in Python:-
Python
data types are different in some aspects from other programming
languages.
It is simple to understand and easy to use. Because Python is
interpreted programming language and Python interpreter can determine which
type of data are storing, so no need to define the data type of memory location.
Every
value in Python has a datatype. Since everything is an object in Python
programming, data types are actually classes and variables are instance
(object) of these classes.
The
data type determines:-
·
The possible values for that type.
·
The operations that can be done with
that values.
·
Conveys the meaning of data.
·
The way values of that type can be
stored.
*There are various data types in Python. Some of the important
types are listed below.
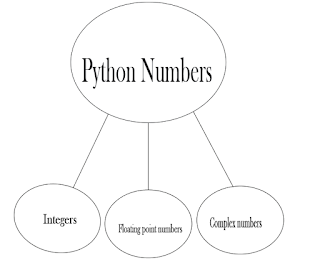
Python Numbers:-
Integers, floating point numbers and
complex numbers falls under Python numbers category.
They are defined as int, float and complex class in Python.
We can use the type() function to know which class a
variable or a value belongs to and the isinstance() function
to check if an object belongs to a particular class.
Integers can be of any length, it is
only limited by the memory available.
A floating point number is accurate
up to 15 decimal places. Integer and floating points are separated by decimal
points. 1 is integer, 1.0 is floating point number.
Complex numbers are written in the
form, x + yj, where x is the real part and y is the imaginary part.
Examples:-
a = 5
print(a, "is of type", type(a))
a = 2.0
print(a, "is of type", type(a))
a = 1+2j
print(a, "is complex number?", isinstance(1+2j,complex))
Comments
Post a Comment